Property zoning
When analysing a site, it is essential to evaluate the zoning regulations that apply to the property. Zoning provides valuable information regarding permits, plans, and potential development opportunities.
You got to check out the zoning to determine whether or not the property has got any permits or whether any existing plan aligns with the zoning requirements. For all these, you must check out what the zoning is.
There are specific overlays and zones where the council will put extra regulations that must be met for you to be able to carry out any development in that area.
What is property zoning?
Property zoning refers to dividing land into different zones or districts, each with specific regulations and permitted uses. Local governments and planning bodies rely on it to manage land use.
Property zoning establishes a framework determining how the land can be utilised, developed, and built upon.
Zoning employs preset categories to assign specific uses to distinct locations. Residential, commercial, industrial, agricultural, and mixed-use zoning are common. Each zone has regulations and restrictions on activities, construction, and development.
Property zoning promotes sustainable development, land use compatibility, and community health, safety, and welfare. Zoning reduces disputes, nuisances, and property values by separating incompatible land uses like industrial and residential.
Australian zoning restrictions in real estate can govern permitted uses, building heights, setbacks, lot sizes, parking, density limits, and architectural design standards.
Local planning bodies enforce local zoning laws. Zoning maps and codes show zones and offer land use and development guidelines.
Zoning laws vary by jurisdiction and can change over time. Property owners and developers must follow zoning restrictions when planning and building. For zoning compliance, permits and approvals may be needed.
You are missing out if you haven’t yet subscribed to our YouTube channel.
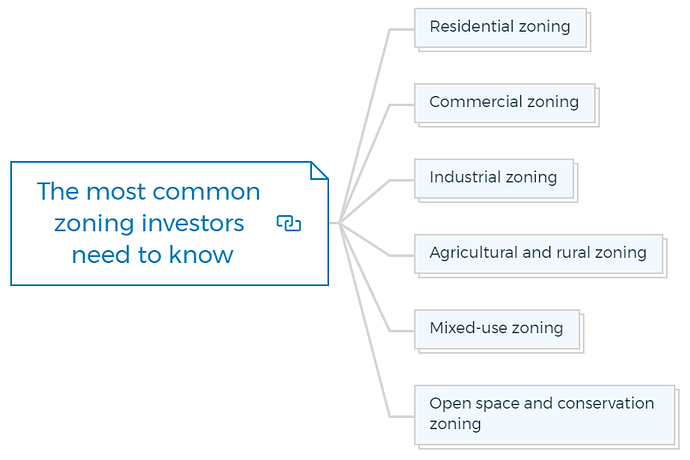
What are the most common zoning investors need to know?
For real estate investors, understanding the most common types of property zoning is crucial when assessing investment opportunities and navigating regulatory requirements.
Here are some of the most common zoning classifications that investors should be aware of:
Residential zoning
Residential zoning designates areas for housing purposes. It can comprise low-density single-family residences, medium-density townhouses or duplexes, and high-density apartment buildings.
Residential zoning often regulates building heights, setbacks, lot sizes, and home-based businesses.
Commercial zoning
Retail stores, offices, and businesses use commercial zoning. Neighbourhood commercial, general commercial, and central business district zoning fall under this category.
Learn More
Industrial zoning
Manufacturing, warehousing, and industrial activities employ industrial zoning. Noise, pollution, and traffic keep these zones from residential neighbourhoods. Industrial zoning might have divisions for light, heavy, and research and development uses.
Agricultural and rural zoning
Farming, ranching, and agricultural activities come under agricultural zoning. It protects farmland, promotes food production, and preserves rural character. Rural zoning may allow low-density housing.
Mixed-use zoning
Mixed-use zoning mixes residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial uses. This zoning encourages small, walkable neighbourhoods and reduces commute. Mixed-use zoning creates lively neighbourhoods where people can live, work, and play.
Open space and conservation zoning
Protecting natural resources, environmentally sensitive areas, and recreational spaces. Parks, woods, wetlands, wildlife habitats, and other protected areas are examples.
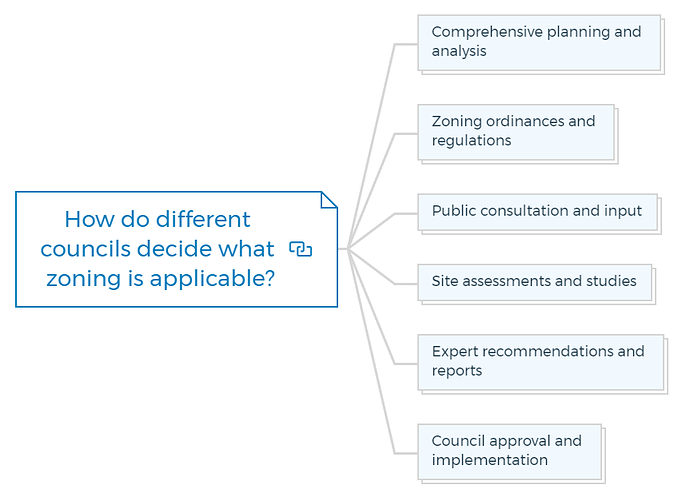
How do different councils decide what zoning is applicable?
Local councils or planning bodies determine zoning. This is a general overview of how councils zone property:
Comprehensive planning and analysis
Local councils prepare long-term visions, goals, and strategies. These plans incorporate population expansion, infrastructural demands, economic development, environmental protection, and community objectives.
Zoning ordinances and regulations
Councils create zoning laws based on comprehensive plans and local planning goals. These documents govern land use and development in their jurisdiction.
They establish zoning categories, allowable uses, building regulations, setbacks, and more.
Public consultation and input
Councils often seek public feedback when zoning property. Residents, community groups, and stakeholders can voice their concerns about proposed zoning changes in public meetings, workshops, or forums.
Public engagement helps ensure zoning choices match local needs and ambitions.
Site assessments and studies
Councils perform site appraisals and studies before zoning changes. Environmental conditions, infrastructural capacity, traffic patterns, and other elements may be assessed.
They inform zoning adjustments and ensure they match the area’s characteristics and limits.
Expert recommendations and reports
Planning professionals, urban designers, architects, and environmental specialists advise local authorities on zoning issues. These professionals analyse proposed zoning changes and help councils make technical choices.
Council approval and implementation
Councils consider proposed zoning amendments after gathering all necessary information. Council or planning committee meetings make final decisions.
If authorised, the council’s formal zoning maps and regulations are updated and enforced by the planning department.
What are zoning overlays?
Zoning overlays add requirements to base zoning. These overlays provide more precise standards and limits depending on area features or concerns.
Zoning overlays change or add to a region’s fundamental zoning. They safeguard features, maintain historic districts, handle environmental challenges, and solve community land use issues.
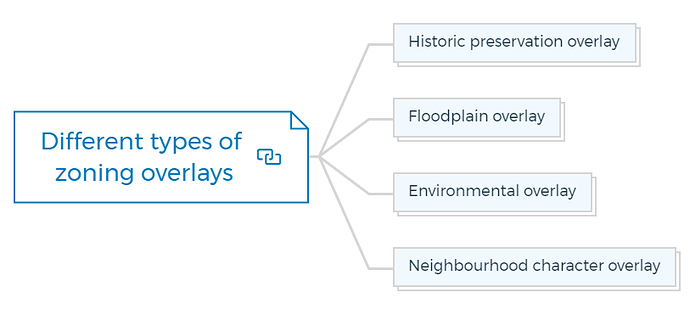
Different types of zoning overlays
Zoning overlays vary by jurisdiction. Some of the common zoning overlays are -
Historic preservation overlay
Historic preservation overlays protect buildings, neighbourhoods, and areas of architectural, cultural, or historical significance.
These overlays often involve design constraints to preserve the area’s charm and legacy.
Floodplain overlay
Floodplain overlays control development in flood-prone areas. They usually limit construction, building heights, and floodplain management.
Environmental overlay
Wetlands, water bodies, endangered species habitats, and high-value biological sites are protected by environmental overlays. These overlays may restrict development to protect the environment and ecological equilibrium.
Neighbourhood character overlay
Neighbourhood character overlays retain a neighbourhood’s particular aesthetics. To maintain neighbourhood character, they may control building design, architectural elements, setbacks, and landscaping.
Impact of zoning overlays on property owners
Zoning overlays can affect property owners in overlay zones. Property alterations, renovations, and new developments may require additional regulations. Property owners must know the overlay’s rules and limits.
How zoning helps property developers and investors?
Property zoning and overlays affect developers’ and investors’ opportunities and restrictions. Developers and investors can gain from property zoning and overlays:
Clarity and predictability
Property zoning defines an area’s land uses, development regulations, and norms. This clarity helps developers and investors plan and execute projects.
Based on approved land uses and development criteria, zoning regulations allow developers to evaluate a project’s feasibility and profitability.
Reduced uncertainty and risk
Zoning restrictions reduce land use and development hazards. Zoning separates incompatible activities into discrete zones, lowering the risk of investing in a property that may encounter conflicts or future zoning changes.
Zoning overlays, such as floodplains or environmental overlays, let developers make educated decisions and avoid risks.
Preservation of property values
Zoning restrictions and overlays ensure compatibility and retain an area’s character, preserving property values.
Zoning limitations help keep properties desirable and marketable by preventing unsuitable or unpleasant land uses near residential zones. By conserving a neighbourhood’s architecture and history, historic preservation overlays can increase property values.
Development of planned communities
Zoning facilitates the creation of mixed-use planned communities. Developers can design mixed-use communities with residential, business, and recreational components with mixed-use zoning.
This can create walkable, dynamic neighbourhoods that attract people, companies, and investors.
Access to incentives and benefits
Zoning regulations may offer incentives and benefits to developers and investors who meet specific standards. These may include density bonuses, financial incentives, quicker permit processing, or the option to negotiate exceptions or variances.
Zoning overlays that promote sustainability or green building may offer incentives or awards for ecologically friendly development.
Community engagement and collaboration
Public discussions during zoning processes help property developers and investors learn about the community’s needs and concerns. Developers can improve their projects’ long-term success by involving the community.
Developers and investors must research, consult with local planning authorities, and seek professional help to manage zoning rules and overlays.
Developers and investors can avoid costly delays, legal challenges, and conflicts by understanding and following zoning laws.
Test Your Knowledge
Property Zoning and Overlays: Understanding and Application Assignment
Objective:
This assignment is designed to help students understand and apply the concepts of property zoning and overlays in real-world scenarios. By completing this assignment, students will demonstrate their ability to navigate zoning regulations, identify opportunities and constraints for development, and understand the impact of zoning on property development and investment.
Instructions:
Complete each section of the assignment by conducting research, analyzing scenarios, and applying the concepts learned from the article on property zoning and overlays. Answer all questions thoroughly and provide examples where possible.
Section 1: Basic Understanding
Define Property Zoning:
In your own words, explain what property zoning is and its purpose. Provide an example of how zoning might affect a property development project.
Types of Zoning:
Describe each of the most common zoning classifications mentioned in the article (residential, commercial, industrial, agricultural and rural, mixed-use, open space and conservation).
For each classification, give an example of a development or use that would be permitted.
Section 2: Zoning Regulations and Compliance
Navigating Zoning Laws:
Choose a local area and research its zoning laws. Identify the zoning district for a specific property and summarize the regulations that apply to it, including any overlays.
Zoning Permits and Approvals:
Describe the process of obtaining zoning permits and approvals for a hypothetical development project within the zoning district you researched. Include steps for ensuring compliance with both base zoning and overlay requirements.
Section 3: Deep Dive into Overlays
Understanding Overlays:
Explain what zoning overlays are and their purpose. Provide an example of an overlay that could impact development plans and how.
Impact Analysis:
Research and find a real-world example where a zoning overlay (such as a historic preservation overlay, floodplain overlay, or environmental overlay) significantly impacted a development project. Describe the project, the overlay restrictions, and how the developers addressed the overlay requirements.
Section 4: Strategic Planning and Investment
Zoning and Property Investment:
Discuss how understanding zoning and overlays can benefit property developers and investors. Include considerations for risk management, property value preservation, and community engagement.
Case Study Analysis:
Find a case study of a successful property development project that navigated zoning regulations and overlays effectively. Summarize the project, the zoning challenges faced, and how the challenges were overcome.
Section 5: Research and Reflection
Future of Zoning:
Conduct research on recent trends or changes in zoning laws and practices, especially those related to sustainability, green building, and mixed-use developments. Discuss how these trends could influence future property development and investment strategies.
Personal Reflection:
Reflect on how an understanding of zoning and overlays could impact your future career in real estate, urban planning, or a related field. Consider the skills and knowledge you would need to navigate these complex regulatory landscapes effectively.
To Do:
Submit your completed assignment as a single document. Include all research sources cited and ensure your work is clearly organized and well-written.
Prepare a 5-minute presentation summarizing your key findings and insights from the assignment. Highlight the case study and personal reflection sections.
Submission Guideline:
This assignment will not only test your understanding of property zoning and overlays but also enhance your research, analysis, and critical thinking skills. Submit it via email or comments.