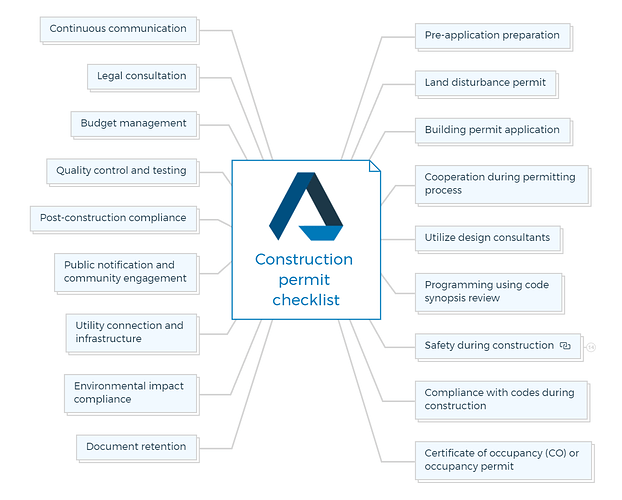
Comprehensive construction permit checklist
This checklist covers key aspects of the permitting process, design, safety, and compliance with building codes.
1. Pre-application preparation
- Research local zoning regulations, land use restrictions, and building codes.
- Determine the specific permits required for your project’s scope and location.
2. Land disturbance permit
- Obtain a land disturbance permit if your project involves significant earth-moving activities.
- Provide erosion control measures to prevent soil erosion during construction.
- The following are usually provided and approved to obtain a land disturbance permit -
- Site plans
- Grading, drainage, and hydrology plans and specifications
- Sewer plans and sections
- Site plans to illustrate other utilities
- Erosion control drawings
- Landscape and tree protection drawings
- Other plans are required for the illustration of flood plains.
You are missing out if you haven’t yet subscribed to our YouTube channel.
3. Building permit application
- Gather all required documents, including architectural plans, engineering drawings, site plans, and project specifications.
- Complete the building permit application form accurately and thoroughly.
4. Cooperation during permitting process
- Maintain open communication with local authorities, zoning boards, and relevant government agencies.
- Address any feedback or concerns raised during the permit review process promptly.
5. Utilize design consultants
- Engage experienced architects, engineers, and consultants to ensure your plans meet local regulations and building codes.
6. Programming using code synopsis review
- Develop a clear project program that outlines the construction’s purpose, layout, and specifications.
- Review local building codes and zoning ordinances to ensure compliance.
- The synopsis should consider the following -
- Area limitations
- Building types
- Construction types
- Dead-end distances
- Exit requirements
- Exit units
- Fire protection systems
- Floor, wall, column, and beam fire resistance ratings
- Handicapped requirements
- Height limitations
- Minimum travel distance to exists
- Required hardware
- Required opening protection
- Separation requirements
- Smoke ventilation and detection requirements
- Structural loading requirements
- Unusual electrical requirements
- Unusual mechanical requirements
- Unusual plumbing requirements
- Use groups
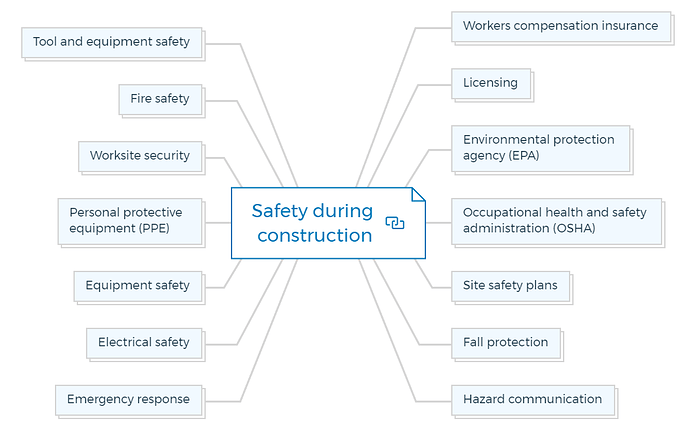
7. Safety during construction
7.1. Workers compensation insurance
- Ensure that all contractors, subcontractors, and workers have valid workers’ compensation insurance to cover injuries and accidents on the construction site.
- Verify that insurance policies are up-to-date and provide adequate coverage.
7.2. Licensing
- Confirm that all contractors, subcontractors, and workers possess the necessary licenses and certifications required by local and state authorities.
- Verify the authenticity of licenses to prevent potential legal and safety issues.
7.3. Environmental protection agency (EPA):
- Adhere to environmental regulations set by the EPA to prevent pollution, hazardous waste, and other environmental risks during construction.
- Implement erosion and sediment control measures to protect nearby water bodies from soil runoff.
7.4. Occupational health and safety administration (OSHA)
- Follow OSHA guidelines and regulations to ensure a safe working environment for all construction personnel.
- Provide necessary safety training, protective equipment, and tools to minimize the risk of accidents and injuries.
7.5. Site safety plans
- Develop and implement a comprehensive site-specific safety plan that outlines safety procedures, emergency protocols, and hazard assessments.
- Clearly communicate the safety plan to all workers and contractors.
7.6. Fall protection
- Install proper fall protection systems, such as guardrails, safety nets, and personal fall arrest systems, when working at heights.
- Train workers on the correct use of fall protection equipment.
7.7. Hazard communication
- Ensure that hazardous materials on-site are properly labelled, stored, and communicated to workers.
- Provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for hazardous substances as OSHA requires.
7.8. Emergency response
- Establish clear emergency procedures, including fires, chemical spills, medical incidents, and natural disasters.
- Keep emergency contact information readily available and conduct regular drills.
7.9. Electrical safety
- Inspect electrical installations to ensure compliance with safety standards and prevent electrical hazards.
- Encourage safe practices when working with electrical equipment and wiring.
7.10. Equipment safety
- Regularly inspect and maintain construction equipment to ensure safe operation.
- Train operators on proper equipment usage and safety measures.
7.11. Personal protective equipment (PPE):
- Mandate appropriate PPE, such as helmets, gloves, eye protection, and high-visibility clothing, based on the nature of the work.
7.12. Worksite security
- Implement measures to prevent unauthorized access to the construction site, reducing the risk of accidents and theft.
7.13. Fire safety
- Install fire extinguishers, alarms, and proper evacuation routes throughout the site.
- Conduct fire safety drills to ensure all workers are familiar with emergency procedures.
7.14. Tool and equipment safety
- Ensure that all tools and equipment are well-maintained, properly stored, and used according to safety guidelines.
- Train workers on safe tool handling practices.
8. Compliance with codes during construction
- Regularly inspect the construction site to ensure compliance with approved plans, building codes, and safety regulations.
- Keep records of all construction activities, inspections, and any modifications made during construction.
- Familiarize yourself with commonly used building codes such as the International Building Code (IBC), International Residential Code (IRC), and National Electrical Code (NEC).
9. Certificate of occupancy (CO) or occupancy permit
- Apply for a CO or occupancy permit upon completion of construction and before occupancy.
- Provide evidence that the project complies with all regulations and is safe for habitation or use.
10. Document retention
- Maintain copies of all submitted documents, permits, and approvals for future reference and potential audits.
11. Environmental impact compliance
- Ensure compliance with environmental regulations, especially if the project involves sensitive areas or natural resources.
12. Utility connection and infrastructure
- Coordinate with utility providers to ensure proper connections for water, electricity, gas, sewage, and other essential services.
13. Public notification and community engagement
- If required, notify neighboring properties about construction activities that might affect them.
- Address community concerns and feedback to foster positive relationships.
14. Post-construction compliance
- Conduct a final inspection to confirm that the construction matches the approved plans and complies with all regulations.
- Rectify any discrepancies or non-compliance issues before obtaining final approvals.
15. Quality control and testing
- Ensure that all materials used meet quality standards and that necessary tests (e.g., structural integrity, fire safety) are conducted and documented.
16. Budget management
- Allocate sufficient funds for permits, inspections, and any unexpected compliance-related costs.
17. Legal consultation
- Consider consulting legal experts to navigate complex permitting processes, especially for large or unique projects.
18. Continuous communication
- Maintain ongoing communication with contractors, designers, consultants, and local authorities to ensure all parties are informed and aligned.