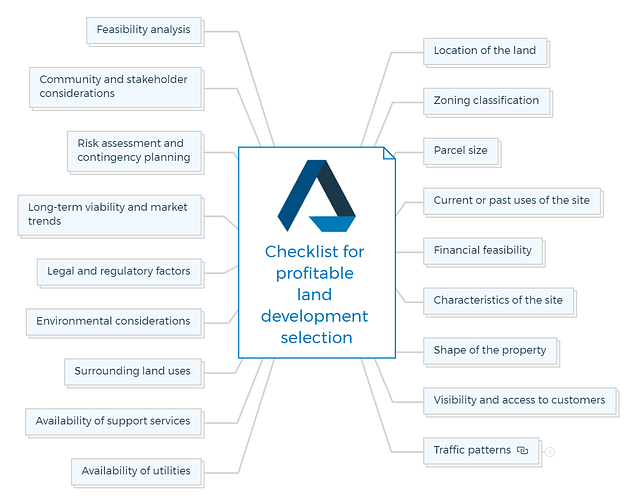
Checklist for profitable land development selection
1. Location of the land
- Evaluate proximity to critical infrastructure (roads, highways, public transportation, airports).
- Assess accessibility to major urban centres and markets.
- Identify potential for growth and development in the area.
- Consider neighbourhood characteristics and demographics.
You are missing out if you haven’t yet subscribed to our YouTube channel.
2. Zoning classification
- Determine compatibility with intended land use and development plans.
- Ensure compliance with local zoning regulations and restrictions.
- Explore possibilities for rezoning if required.
3. Parcel size
- Verify whether the land size is adequate for the intended development.
- Consider setbacks, parking requirements, and open space provisions.
4. Current or past uses of the site
- Investigate the environmental impact due to past or current land uses.
- Evaluate the potential for contamination and remediation.
5. Financial feasibility
- Check alignment with the project budget and financial feasibility.
- Conduct a comparative analysis of land prices in the surrounding area.
6. Characteristics of the site
- Examine topography, soil conditions, and drainage.
- Account for natural features like water bodies and vegetation, assessing their impact.
- Address elevation and flood risk with a thorough assessment.
7. Shape of the property
- Assess how well the property’s shape suits the desired layout and design.
- Understand the implications for efficient space utilization and ease of access.
8. Visibility and access to customers
- Gauge proximity to major roads, intersections, and transportation hubs.
- Ensure clear sightlines for effective advertising and signage.
- Assess the ease of entry and exit for customers and visitors.
9. Traffic patterns
- Study ingress and egress points from the site.
- Note nearby road and street speed limits.
- Analyze traffic counts and flow during peak hours.
- Evaluate the presence and impact of traffic lights, signals, and intersections.
In-depth traffic analysis: Curb and median cuts
- Examine the availability and placement of curb cuts.
- Assess accessibility for vehicle entrance and exit.
- Understand the implications of median cuts on traffic flow and safety.
10. Availability of utilities
- Determine access to essential utilities such as water, sewer, electricity, and gas.
- Evaluate the feasibility of connecting to existing utility infrastructure.
- Consider potential costs associated with utility installation and hookup.
11. Availability of support services
- Identify nearby availability of emergency services (fire, police, medical).
- Assess proximity to retail, dining, and other amenities.
- Consider accessibility to schools, healthcare facilities, and public services.
12. Surrounding land uses
- Check compatibility with neighbouring properties and land uses.
- Assess the potential for synergy or conflict with nearby developments.
- Consider how future developments impact the site’s value and functionality.
13. Environmental considerations
- Prioritize the preservation of natural habitats and ecosystems.
- Ensure compliance with environmental regulations and permits.
- Plan for mitigation of potential negative impacts on the environment.
14. Legal and regulatory factors
- Ensure adherence to local, state, and federal laws and regulations.
- Guide the process of navigating permitting and approval procedures.
- Understand any existing easements, restrictions, or encumbrances on the property.
15. Long-term viability and market trends
- Analyze current and projected market demand for the proposed development.
- Anticipate changes in demographics, technology, and economic trends.
- Evaluate the potential for sustained profitability over the project’s lifecycle.
16. Risk assessment and contingency planning
- Identify potential risks and challenges associated with the site.
- Formulate strategies to mitigate or manage these risks.
- Allocate resources to address unexpected obstacles.
17. Community and stakeholder considerations
- Emphasize engagement with the local community and stakeholders.
- Address concerns, feedback, and input from neighboring residents and businesses.
- Build positive relationships and goodwill within the community.
18. Feasibility analysis
- Conduct a holistic evaluation of the site’s potential for successful development.
- Perform financial analysis, including estimated costs, revenues, and return on investment.
- Compare the site against alternative options to make informed decisions.
Learn More
This comprehensive checklist equips property developers, investors, and realtors with a strategic framework for assessing and selecting land for development.