Checklist for financial feasibility approaches
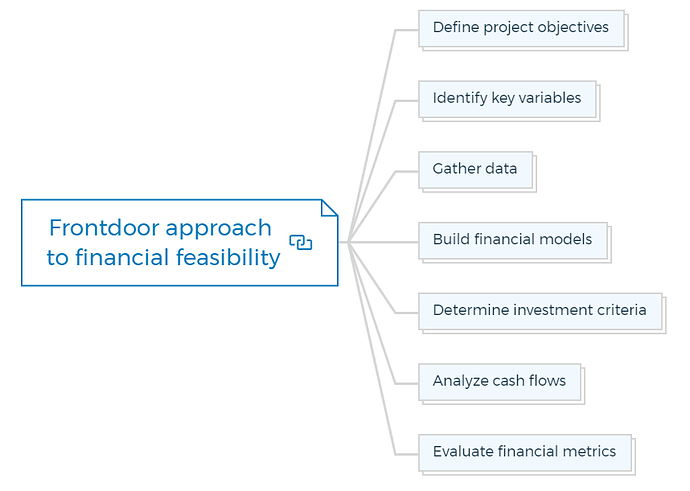
1. Frontdoor approach to financial feasibility
1.1. Define project objectives
Clearly outline the goals and objectives of the project to guide the feasibility assessment.
1.2. Identify key variables
Identify the critical factors that will impact the financial feasibility of the project, such as revenues, costs, and market conditions.
1.3. Gather data
Collect accurate and reliable data related to costs, revenues, market trends, and financing options.
1.4. Build financial models
Develop financial models that project cash flows, net operating income (NOI), and potential returns based on different scenarios.
1.5. Determine investment criteria
Define the investment criteria, such as minimum required return on investment (ROI) or payback period, to assess project feasibility.
1.6. Analyze cash flows
Calculate cash inflows and outflows over the project’s lifespan, considering operational costs, financing expenses, and income streams.
1.7. Evaluate financial metrics
Assess financial indicators like Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Profitability Index to determine project viability.
You are missing out if you haven’t yet subscribed to our YouTube channel.
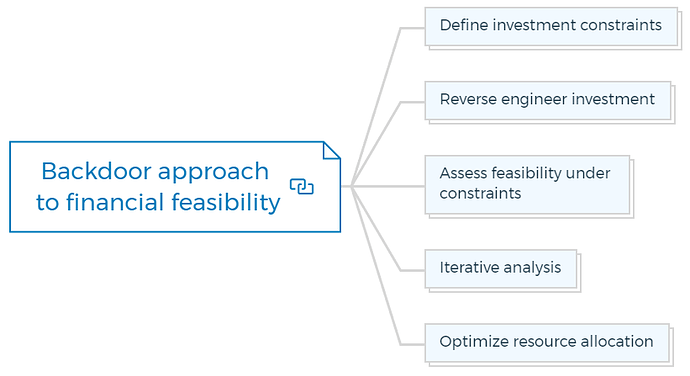
2. Backdoor approach to financial feasibility
2.1. Define investment constraints
Specify any limitations or constraints, such as budget constraints or maximum acceptable risk level.
2.2. Reverse engineer investment
Begin with the maximum investment budget and work backward to determine the project’s feasibility, factoring in costs, financing, and desired returns.
2.3. Assess feasibility under constraints
Evaluate whether the project meets the defined investment constraints while achieving satisfactory financial performance.
2.4. Iterative analysis
If the project exceeds constraints, iteratively adjust the project parameters (e.g., costs, revenue projections) until the project aligns with the constraints.
2.5. Optimize resource allocation
Optimize the allocation of resources to maximize financial feasibility within the defined constraints.
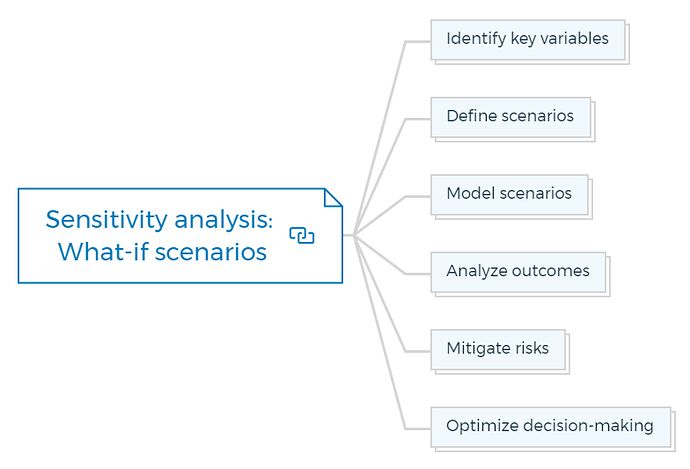
3. Sensitivity analysis: What-if scenarios
3.1. Identify key variables
Determine the variables that have the most significant impact on the project’s financial feasibility, such as sales volume, rent rates, or interest rates.
3.2. Define scenarios
Create different scenarios by varying the identified key variables to understand how changes affect financial outcomes.
3.3. Model scenarios
Adjust the financial models to reflect the changes in variables for each scenario, including impacts on cash flows, NPV, and IRR.
3.4. Analyze outcomes
Assess the results of each scenario to understand potential risks, opportunities, and how sensitive the project’s feasibility is to changes in variables.
3.5. Mitigate risks
Identify strategies to mitigate risks associated with unfavorable scenarios, such as adjusting project design, pricing, or financing options.
3.6. Optimize decision-making
Use sensitivity analysis to make informed decisions by understanding the range of possible outcomes and their implications.