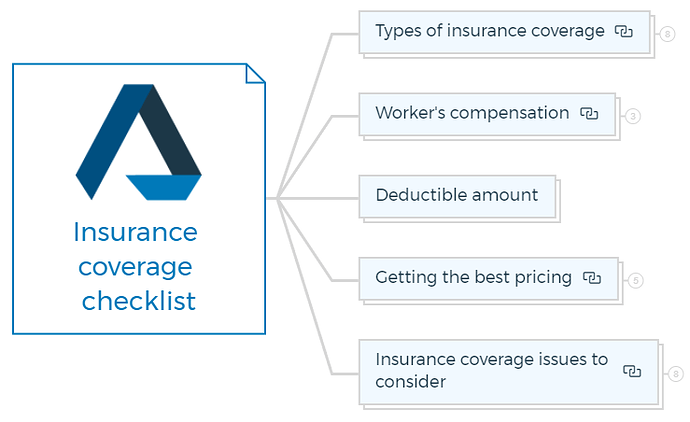
Before completing a development project, it is crucial to ensure that you have the right insurance coverage in place to protect your interests and assets. Here is the detailed checklist to help you navigate the various types of insurance coverage, considerations, and best practices for obtaining the best pricing:
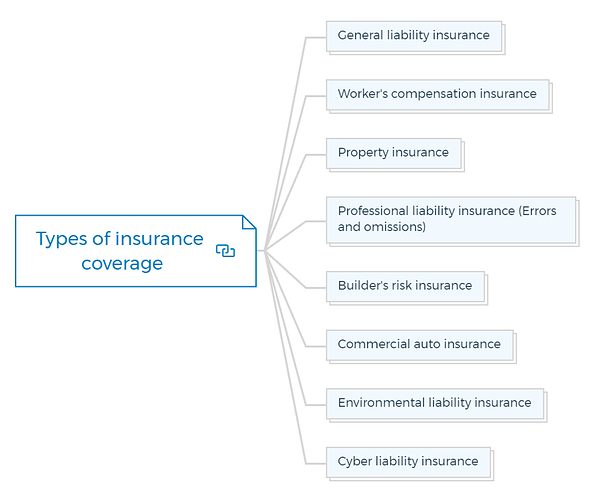
Types of insurance coverage
1. General liability insurance:
- Determine the coverage limit required based on project size and risks.
- Verify if the policy covers bodily injury, property damage, and personal/advertising injury.
2. Worker’s compensation insurance
- Ensure that all employees, including subcontractors, are covered.
- Confirm the compliance with local labor laws and regulations.
- Provide accurate employee payroll information to calculate premiums.
3. Property insurance
- Calculate the property value accurately, including buildings, equipment, and materials.
- Understand the property insurance deductible, which is the amount you must pay out of pocket before coverage kicks in.
4. Professional liability insurance (Errors and omissions)
- Determine if it’s necessary based on the type of work performed.
- Define the scope of coverage, especially if subcontractors are involved.
5. Builder’s risk insurance
- Assess if this coverage is required for new construction or significant renovations.
- Determine the coverage period and any limitations.
- Verify if natural disasters (e.g., earthquakes, floods) are included.
6. Commercial auto insurance
- Ensure all vehicles used for the project are covered.
- Verify if hired or non-owned auto coverage is necessary.
7. Environmental liability insurance
- Evaluate the need for coverage related to environmental risks or pollution liability.
8. Cyber liability insurance
- Consider this if your project involves sensitive data or digital systems.
You are missing out if you haven’t yet subscribed to our YouTube channel.
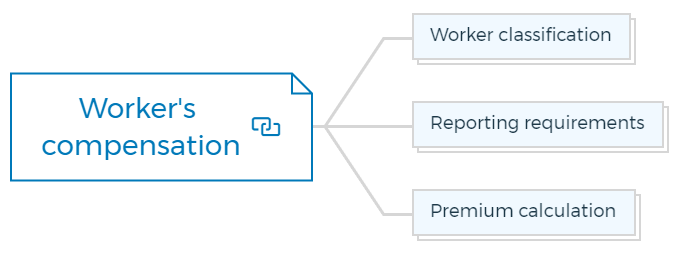
Worker’s compensation
1. Worker classification
- Accurately classify workers as employees or independent contractors to determine coverage requirements.
2. Reporting requirements
- Understand the process for reporting injuries and claims to the insurance provider.
3. Premium calculation
- Provide detailed payroll records to calculate premiums accurately.
Deductible amount
- Know the exact amount of the property insurance deductible.
- Consider your financial capacity to cover the deductible in the event of a claim.
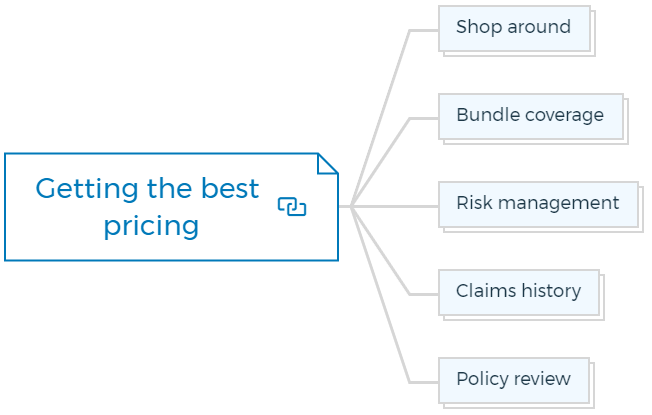
Getting the best pricing
1. Shop around
- Obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers.
- Consider using an insurance broker for expert advice and negotiation.
2. Bundle coverage
- Explore options to bundle multiple policies with the same provider for potential discounts.
3. Risk management
- Implement robust risk management practices to reduce premiums (e.g., safety training, security measures).
4. Claims history
- Maintain a good claims history to demonstrate your risk management capabilities to insurers.
5. Policy review
- Regularly review and update your policies to ensure they align with your project’s needs.
Insurance coverage issues to consider
1. Policy exclusions
- Understand any exclusions in your policies, such as acts of terrorism or intentional misconduct.
2. Policy limits
- Ensure coverage limits are adequate to protect against potential losses.
3. Certificates of insurance
- Obtain certificates of insurance from subcontractors to verify their coverage.
4. Notice requirements
- Familiarize yourself with policy notice requirements for claims reporting.
5. Renewal and cancellation
- Be aware of policy renewal and cancellation terms and timelines.
6. Document everything
- Maintain thorough records of insurance policies, claims, and communications with insurers.
7. Legal and regulatory compliance
- Ensure that your insurance coverage complies with local, state, and federal laws and regulations.
8. Consult an insurance professional
- Consider seeking advice from an insurance expert or attorney for complex insurance needs.