Understanding Discounted Cashflow (DCF), Present Value (PV), and Net Present Value (NPV) in Real Estate Proforma
1. Discounted Cashflow (DCF)
- Definition: DCF calculates the present value of future cash flows generated by an investment, adjusted for the time value of money.
- Formula:
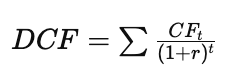
-
Where:
- CFt= cash flow at time t
- r = discount rate
- t = time period
-
Advantages:
- Accounts for the time value of money, reflecting how future cash flows are less valuable today.
- Helps in comparing projects with different time horizons.
- Provides a comprehensive view of the investment’s future cash flows.
-
Disadvantages:
- Highly sensitive to the discount rate; a small change can dramatically impact results.
- Requires accurate cash flow forecasting, which is often uncertain.
-
Good For:
- Valuing investments with long-term cash flows, like real estate development or lease revenue.
-
Shortcomings:
- Subject to cash flow prediction errors and assumptions.
-
Meaning for the Investor:
- Shows the value of future cash flows in today’s terms. If DCF is greater than the initial investment, the project may be considered attractive.
2. Present Value (PV)
- Definition: PV calculates the current value of a single future cash flow or multiple cash flows, discounted at a specific rate.
- Formula:
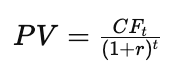
- Advantages:
- Simple to calculate for individual cash flows.
- Helps investors understand how much future money is worth today.
- Flexible and can be applied to any point in time.
- Disadvantages:
- Like DCF, it is sensitive to the discount rate chosen.
- Doesn’t account for the total profitability of the project—only the current value of a specific cash flow.
- Good For:
- Quick calculations to determine the value of future payments, such as rental income or loan repayments.
- Shortcomings:
- Only focuses on specific cash flows, so it doesn’t provide a full picture of project profitability.
- Meaning for the Investor:
- Helps assess how much they need to invest today to receive a certain cash flow in the future.
3. Net Present Value (NPV)
- Definition: NPV calculates the difference between the present value of cash inflows and the initial investment (cash outflows). It shows the net gain or loss in value.
- Formula:
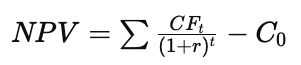
- Where:
- C0 = initial investment
- CFt = cash flow at time t
- r = discount rate
- t = time period
- Advantages:
- Accounts for both cash inflows and the initial investment, providing a clear picture of profitability.
- Considers the time value of money and allows comparison across projects.
- Helps determine whether the project adds value over time.
- Disadvantages:
- Complex if the project involves multiple cash flows or changing discount rates.
- Heavily reliant on discount rate accuracy.
- Good For:
- Making go/no-go decisions on investments based on profitability.
- Shortcomings:
- The choice of discount rate can significantly impact results.
- Does not account for risk beyond the discount rate.
- Meaning for the Investor:
- Positive NPV indicates a potentially profitable project, while negative NPV suggests the investment may not meet the return expectations.
Pros and Cons Overview
| Metric | Pros | Cons | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCF | Accounts for time value of money; compares long-term cashflows | Sensitive to discount rate; requires accurate projections | Long-term investment valuation |
| PV | Simple to calculate; shows current value of future cash flows | Only reflects one cash flow or payment, not entire profitability | Estimating current value of specific cash flows |
| NPV | Comprehensive; considers cash inflows and outflows | Relies heavily on discount rate; complex with multiple flows | Deciding if a project adds value |
Good Ranges for Each
- DCF: Greater than the initial investment means the project is worthwhile.
- PV: Any positive value means the future cash flows are worth investing in today.
- NPV: A positive NPV signals a profitable project, while a negative NPV may indicate the need for revaluation.
What Does This Mean for Investors?
- DCF: Helps in understanding whether long-term projects (like real estate development) are valuable when considering future cash flows.
- PV: Gives clarity on how much future revenue is worth today.
- NPV: The ultimate measure of whether an investment is expected to generate more value than it costs.
