1. Gross Rental Yield
- Definition: Gross rental yield measures the annual income generated by a property as a percentage of its purchase price. It’s calculated using the formula:
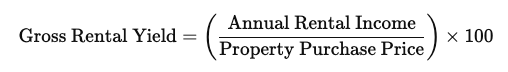
- Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Advantages:
- Simple to calculate.
- Provides a quick estimate of rental income potential.
- Disadvantages:
- Does not account for operating expenses, such as maintenance, property taxes, or vacancies.
- Advantages:
- Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Offers a rough estimate of property profitability.
- Cons: May be misleading as it overestimates profitability by ignoring costs.
- Shortcomings:
- It does not consider any expenses, leading to an inflated picture of profitability.
- Good for:
- Quick comparisons between properties to identify high-yield opportunities.
- Good Range:
- Typically, 5% to 10% is considered a solid range for gross rental yield, depending on market conditions.
2. Net Rental Yield
- Definition: Net rental yield measures the annual rental income after deducting all property-related expenses, expressed as a percentage of the property purchase price. The formula is:

- Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Advantages: Provides a more accurate estimate of profitability by accounting for expenses.
- Disadvantages: Requires detailed information on expenses, making it more complex to calculate.
- Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Offers a realistic view of investment performance.
- Cons: Harder to estimate upfront if not all expenses are known.
- Shortcomings:
- May still overlook some expenses like large-scale maintenance or unexpected costs.
- Good for:
- Evaluating the actual cash flow and performance of a rental property.
- Good Range:
- A range of 4% to 8% is often seen as healthy, though this can vary by market.
3. Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM)
- Definition: Gross Rent Multiplier is a simple measure of a property’s value based on its gross rental income. It is calculated as:

- Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Advantages: Easy to calculate and useful for quick comparisons.
- Disadvantages: Does not account for expenses, making it less precise for profitability analysis.
- Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Useful for quick evaluations and comparisons.
- Cons: Does not reflect operating costs or potential risks.
- Shortcomings:
- Oversimplifies profitability by ignoring net income.
- Good for:
- Screening potential investments quickly.
- Good Range:
- Generally, a lower GRM indicates a better deal. A GRM below 10 is typically favorable, though it depends on the local market.
4. Net Income Multiplier (NIM)
- Definition: Net Income Multiplier measures a property’s value relative to its net operating income. It is calculated as:

- Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Advantages: Considers net income, providing a more accurate reflection of the property’s profitability.
- Disadvantages: Requires detailed and accurate NOI calculation.
- Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Provides a more precise estimate of investment value.
- Cons: Complexity in estimating NOI if all expenses are not known.
- Shortcomings:
- Assumes that all expenses are accurately calculated, which may not always be the case.
- Good for:
- In-depth analysis of a property’s actual profitability.
- Good Range:
- Typically, a lower NIM is more attractive, with ranges varying widely depending on the market.